CASE statement, an expression to evaluate different conditions to return a scalar value, when a condition is met. If none of the condition evaluated to TRUE then expression from ELSE block will be returned. Although ELSE block is optional. Above all, the CASE statement have two formats Simple CASE & Searched CASE.
This tech-recipes post highlights the use of the Searched CASE statement. Including search and pattern matching to fetch the results.
CASE statement format
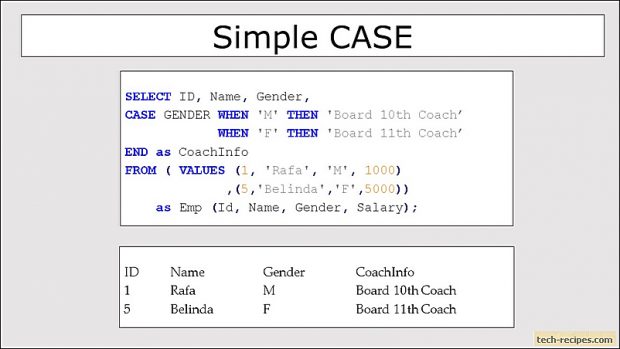
1. Simple CASE
Instead of writing nested IF statement to compare multiple expressions we can use simple CASE expression. In this format, simple CASE expression compares the first expression to the expression in the WHEN clause. If an equal match is found then expression after THEN is evaluated otherwise expression in the ELSE block gets evaluated. Note that ELSE block is optional.
Syntax
CASE WHEN input_expression = when_expression THEN output_expression WHEN input_expression = when_expression THEN output_expression [Optional] ELSE output_expression END
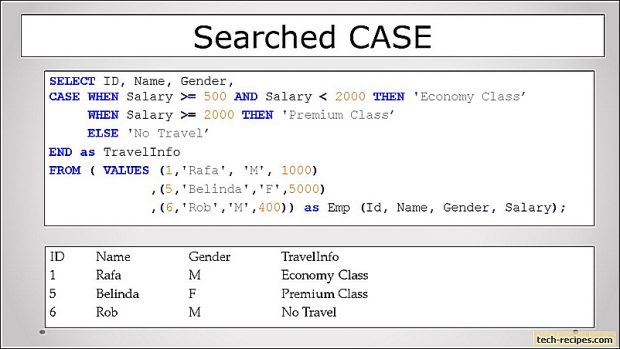
2. Searched CASE
Searched CASE, extended SIMPLE case. This evaluates set of boolean expressions including pattern matching, rang comparisons. If any of the boolean expression evaluates to TRUE then expression after THEN gets evaluated. ELSE block is optional, evaluates if none of the boolean expression after WHEN evaluates to TRUE.
CASE WHEN boolean_expression THEN output_expression WHEN boolean_expression THEN output_expression [Optional] ELSE output_expression END
Examples
Above all, let us do a walkthrough for Simple and Searched CASE with the following examples. Using VALUES constructor to build a temporary result set of employees.
1.
Simple CASE Expression
In the following example, matching M and F values against the GENDER column. Simple comparison, for the first 3 rows, having M gender assigned 10th coach. Rest of the 2 rows, having F gender assigned 11th coach.
SELECT ID, Name, Gender, Salary, CASE GENDER WHEN 'M' THEN 'Board 10th Coach' WHEN 'F' THEN 'Board 11th Coach' END as CoachInfo FROM (VALUES (1,'Vish', 'M', 100) ,(2,'Atul', 'M', 200) ,(3,'Vishal','M', 500) ,(4,'Kasturi','F',2000) ,(5,'Belinda','F',5000)) as Emp(Id, Name, Gender, Salary);
ID Name Gender Salary CoachInfo ----------- ------- ------ ----------- ---------------- 1 Vish M 100 Board 10th Coach 2 Atul M 200 Board 10th Coach 3 Vishal M 500 Board 10th Coach 4 Kasturi F 2000 Board 11th Coach 5 Belinda F 5000 Board 11th Coach (5 rows affected)
2.
Searched CASE Expression
In this example, boolean searched case does a range comparison. On the basis of the Salary column. The searched case will evaluate a boolean expression and if its TRUE then expression after THEN is performed. If none of the rows evaluates to TRUE then optional ELSE block is taken into consideration.
Here, salary greater than equal to 500 and less than 2000 falls under economy class. Furthermore, salary greater than equal to 2000 falls under premium class. If the salary is not within a defined range then ELSE block with no travel is displayed.
SELECT ID, Name, Gender, Salary, CASE WHEN Salary >= 500 AND Salary < 2000 THEN 'Economy Class' WHEN Salary >= 2000 THEN 'Premium Class' ELSE 'No Travel' END TravelMode FROM (VALUES (1,'Vish', 'M', 100) ,(2,'Atul', 'M', 200) ,(3,'Vishal','M', 500) ,(4,'Kasturi','F',2000) ,(5,'Belinda','F',5000)) as Emp(Id, Name, Gender, Salary);
ID Name Gender Salary TravelMode ----------- ------- ------ ----------- ------------- 1 Vish M 100 No Travel 2 Atul M 200 No Travel 3 Vishal M 500 Economy Class 4 Kasturi F 2000 Premium Class 5 Belinda F 5000 Premium Class (5 rows affected)
3.
Searched CASE Expression With IN, OR and LIKE Operator
This example demonstrates the use of different clauses and operator with CASE expression. In the below query, we can see the use of IN, OR and LIKE operator for comparison and pattern matching. IN and OR operator nearly similar in this case. LIKE gives us the flexibility to use pattern matching.
SELECT ID, Name, Gender, Salary, CASE WHEN Name IN ('Atul', 'Belinda') THEN 'Class 1' WHEN Name LIKE 'K%' THEN 'Class 2' WHEN (NAME = 'Vish' OR Name = 'Vishal') THEN 'Class 3' ELSE 'No Class' END as ClassInfo FROM (VALUES (1,'Vish', 'M', 100) ,(2,'Atul', 'M', 200) ,(3,'Vishal','M', 500) ,(4,'Kasturi','F',2000) ,(5,'Belinda','F',5000) ,(5,'Simona','M',5000)) as Emp(Id, Name, Gender, Salary);
ID Name Gender Salary ClassInfo ----------- ------- ------ ----------- --------- 1 Vish M 100 Class 3 2 Atul M 200 Class 1 3 Vishal M 500 Class 3 4 Kasturi F 2000 Class 2 5 Belinda F 5000 Class 1 5 Simona M 5000 No Class (6 rows affected)
4.
Searched CASE Expression with CHARINDEX & PATINDEX
Similarly, using CHARINDEX and PATINDEX function with searched CASE. Following example demonstrates the use of CHARINDEX function to find if a character exists in any name. Using PATINDEX for pattern matching to find if _ (Underscore) exists anywhere in the name column.
SELECT ID, Name, Gender, Salary, CASE WHEN CHARINDEX('s', Name) > 0 THEN 'Contains char s' WHEN PATINDEX('%_%',Name) > 0 THen 'Underscore Exists' ELSE 'Optional' END as ClassInfo FROM (VALUES (1,'Vish', 'M', 100) ,(2,'Atul_', 'M', 200) ,(3,'Vishal','M', 500) ,(4,'Kasturi','F',2000) ,(5,'Belinda_','F',5000) ,(5,'Simona','M',5000)) as Emp(Id, Name, Gender, Salary);
ID Name Gender Salary ClassInfo ----------- -------- ------ ----------- ----------------- 1 Vish M 100 Contains char s 2 Atul_ M 200 Underscore Exists 3 Vishal M 500 Contains char s 4 Kasturi F 2000 Contains char s 5 Belinda_ F 5000 Underscore Exists 5 Simona M 5000 Contains char s (6 rows affected)
5.
Searched CASE Expression with ORDER BY
An earlier post on tech-recipes included the use of CASE with ORDER BY in detail with many examples. Here adding CASE expression to ORDER BY clause to sort Belinda name first followed by other names in ascending order. Without using CASE we can not sort Belinda first in the list.
SELECT ID, Name, Gender, Salary FROM (VALUES (1,'Vish', 'M', 100) ,(2,'Atul', 'M', 200) ,(3,'Vishal','M', 500) ,(4,'Kasturi','F',2000) ,(5,'Belinda','F',5000) ,(5,'Simona','M',5000)) as Emp(Id, Name, Gender, Salary) ORDER BY CASE WHEN NAME = 'Belinda' THEN 0 ELSE 1 END, Name;
ID Name Gender Salary ----------- ------- ------ ----------- 5 Belinda F 5000 2 Atul M 200 4 Kasturi F 2000 5 Simona M 5000 1 Vish M 100 3 Vishal M 500 (6 rows affected)
Summary
As a result in this tech-recipes post we have learned Searched CASE expression. Simple and Searched cases are two common formats. With extended pattern maching and use of function allows us to do more with Searched case compared to Simple. Furthermore, most of the function works with Searched CASE to do more. If you like this post you may want to browse through Tech-recipes Database archive posts.