Networking is not as hard as it sounds, especially the introductory part is very easy and interesting. In the previous tech-recipes, we covered the practical tools used to stimulate networking. We are using HUAWEI eNSP and Wireshark to study networks. This article will cover How data packets constituents can be read in Wireshark.
What is WireShark
Everything we do over the internet travels in the form of data packets. And those data packets know where they need to head. The data is encapsulated with frames. The frames consist of headers and trailers which have all sorts of information for example to which network they have to move, how big the data is, etc.
As mentioned in previous articles, the data transfers on the basis of protocols that are set and agreed on by both the parties that are exchanging the data. Protocols are a set of rules. Observing the sequence of messages exchanged between two protocol entities, delving down into the details of protocol operation, and causing protocols to perform certain actions and then observing these actions and their consequences.
It is important for any network analyst to understand the exact constituents of data packets. We can simulate a network, send data, and halfway through we catch those data packets and pop open each of the header and trailer to see the constituents of the data packet.
The basic tool for observing the exchange of messages between executing protocol entities is called a packet sniffer. As the name suggests, a packet sniffer captures (“sniffs”) messages being sent/receive from/by your computer; it will also typically store and/or display the contents of the various protocol fields in these captured messages.
Check out this article to set up a small network.How to Establish a Single Switched Network. Once you set up a network of two computers using a copper wire, and send some data from one device to the other, we need to follow the below steps
How to Read Data Packet Constituents in Wireshark
Step-by-Step Tutorial
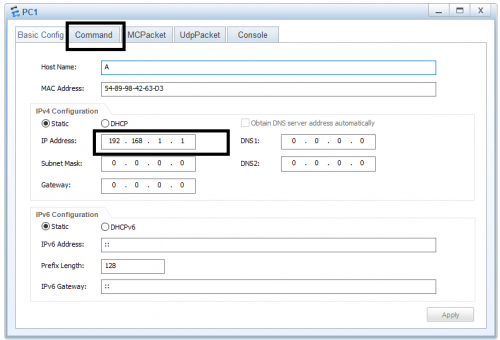
1. You have to make a few configuration settings for each of the devices. Click on one of the devices and open settings. Set the IP address, make sure you have the same network address for both devices, 192.168.1.1 for this device.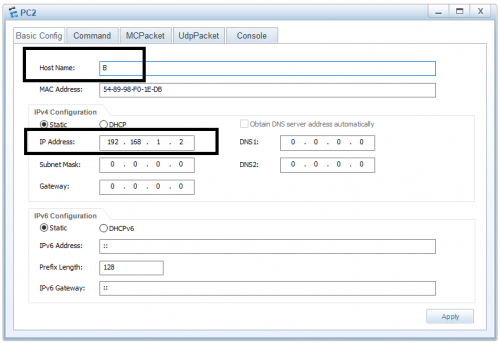
2. For the other device open the settings and write the IP address, change the host address from the above IP address. i.e set the host address to 192.168.1.2. If you have no idea about the divine of IP address you can check out this tech recipe where I explained the IP and MAC address. Once the configuration is done click on the command to open the command line
3. Now to send data from one device to another simply ping one device from the other. On-device ping device B.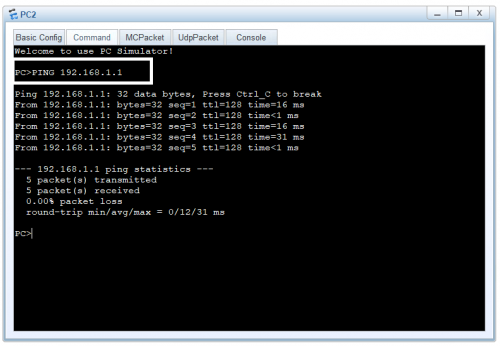
4. Now capture the data on the other device. This will open the Wireshark window, which will sniff the packet to read the constituents of that data. However, you have to ping again once Wireshark opens because the other ping command has already executed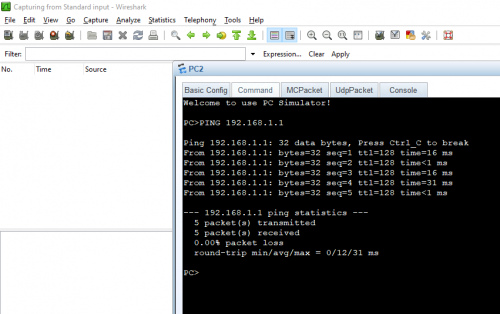
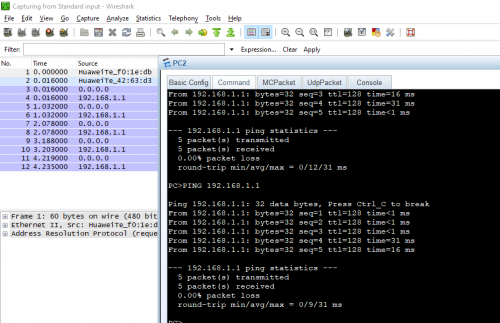
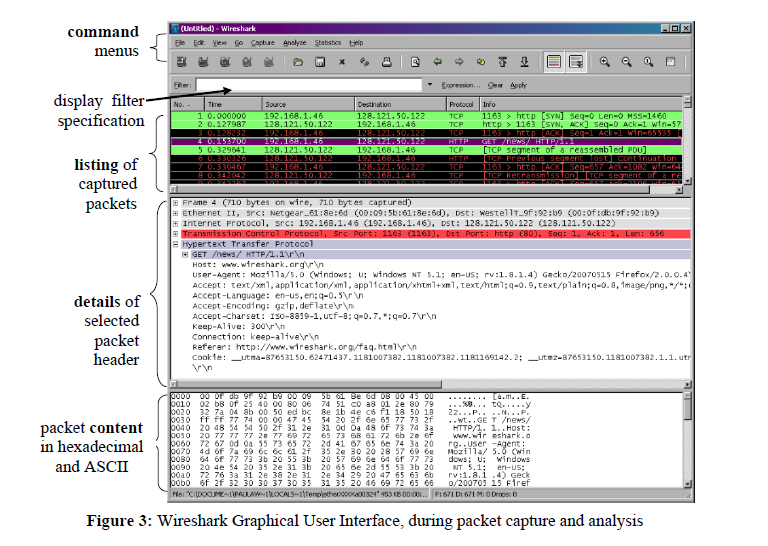
5. The captured data will look like this. Note all the details of the data.
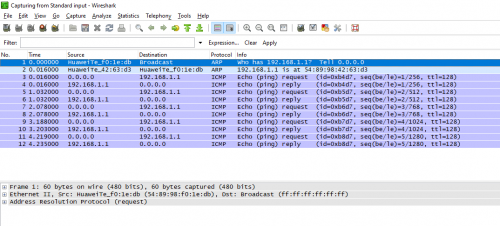
From here you can observe all the constituents of the data. However, the details of the data will occupy the next tech-recipes until then enjoy the other recipes available to you via tech-recipes.